Dryers
Vapco engineers supplies engineering services and complete process plants and components for drying of products to customers in the industries of distillery, food and dairy, chemicals, pharmaceuticals and environmental protection. Drying is one of the most widely used unit operation in the processing industries. Vapco offer a range of dryers for handling fluid, paste, and moist powder, particulate and granulate feeds.

Dryers
- Steam tube dryer:
![]() Rotating shell
Rotating shell
![]() Fixed shell
Fixed shell
- Flash dryer
- Rotary cascade dryer
- Spray dryer
- Belt dryer
- Rotary vacuum dryer
- Paddle dryer
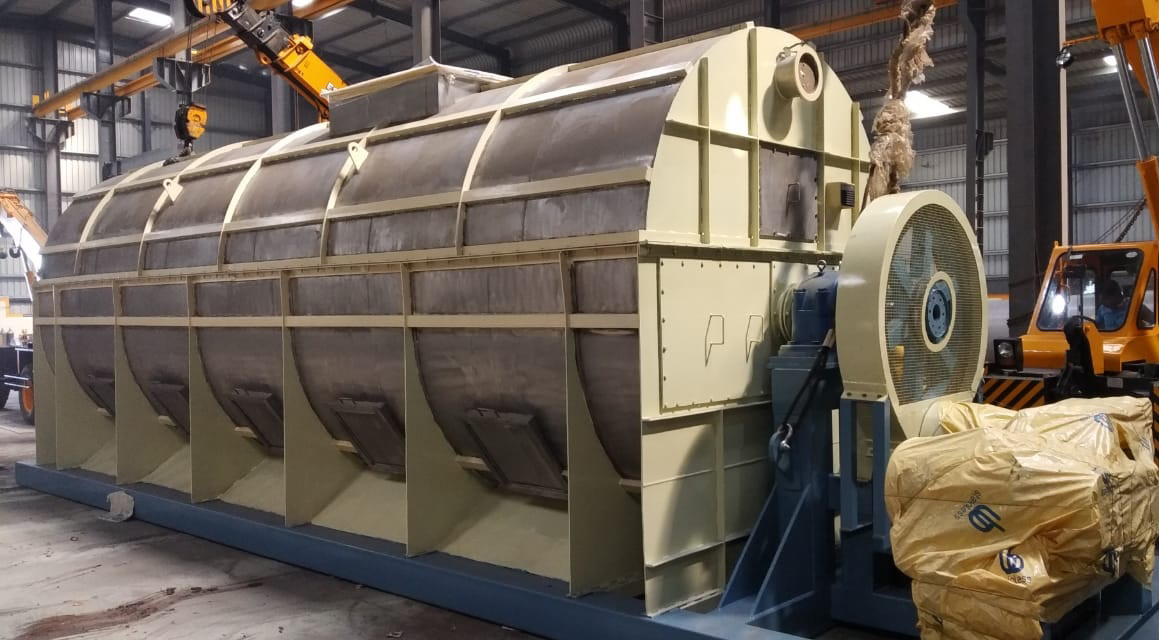
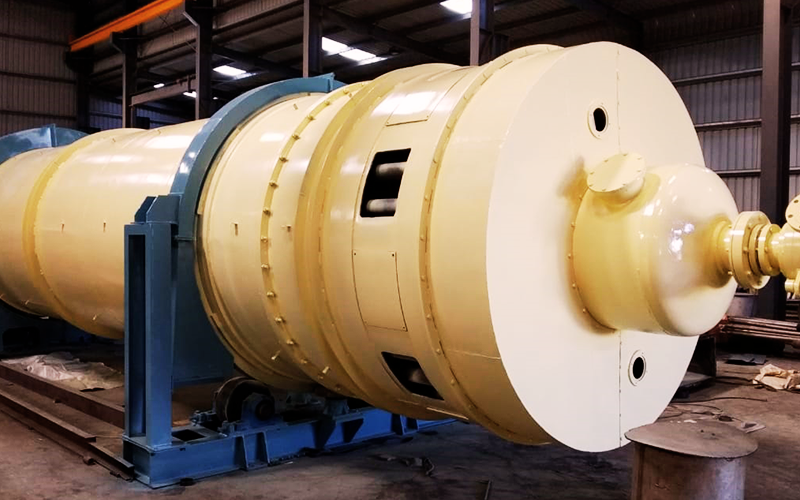
Steam Tube Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- The material is fed continuously at uniform rate and is tumbled & showered by rotation of cylinder.
- In a stream of hot air, when moisture gets transferred to the air, rendering the product progressively dry as it travels the length of the dryer
- The humid air is exhausted into atmosphere via a dust collection system to trap fines escaping with the exhaust air.
Advantages:
![]() Low temperature, indirect drying
Low temperature, indirect drying
![]() Suitable for free flowing granular feeds.
Suitable for free flowing granular feeds.
![]() High thermal efficiency
High thermal efficiency
![]() Minimal process air flow
Minimal process air flow
![]() Relatively low emissions
Relatively low emissions
![]() Adaptability to fluctuating feed rates & moisture contents of products
Adaptability to fluctuating feed rates & moisture contents of products
Applications:
![]() Germ / Fiber
Germ / Fiber
![]() DDGS / Spent Grain
DDGS / Spent Grain
![]() Fly ash
Fly ash
![]() Agro products
Agro products


Flash Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- In the flash dryer, particles are dispersed by different means depending on the product into a hot air stream at high velocity conveying and drying the product to a free flowing powder in a very short time.
- This design uses suspended particle drying techniques where surface moisture of the material is rapidly removed by dispersing the particulate solids in a heated stream of gas / air.
- The drying economy is very dependent upon the source of energy and the maximum allowable inlet temperatures.
Advantages:
![]() Suitable for drying dewatered solids
Suitable for drying dewatered solids
![]() High Heat Transfer coefficient & Thermal efficiency
High Heat Transfer coefficient & Thermal efficiency
![]() Quick plant start-up and adjustment of operating conditions
Quick plant start-up and adjustment of operating conditions
![]() Excellent choice for processing heat-sensitive or easily oxidized feed materials
Excellent choice for processing heat-sensitive or easily oxidized feed materials
![]() Easy to change product or product grade with minimum downtime
Easy to change product or product grade with minimum downtime
![]() Efficient & simple process control system
Efficient & simple process control system
![]() Quick response to operational changes
Quick response to operational changes
Applications:
![]() Dye Intermediates
Dye Intermediates
![]() Starch
Starch
![]() Gluten
Gluten
Rotary Cascade Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- Drying, roasting or heat treatment is achieved by passing the material being processed through a rotating cylinder through which also passes a current of hot air.
- Lifters or flights fitted to the internal surface of the cylinder lift and cascade the material through the hot air stream.
- The air stream can be directed through the cylinder either co-current or counter-current manner.
Advantages:
![]() Suitable for free flowing granular feeds.
Suitable for free flowing granular feeds.
![]() Low power demand.
Low power demand.
![]() Quick plant start-up and adjustment of operating conditions.
Quick plant start-up and adjustment of operating conditions.
![]() High Thermal efficiency.
High Thermal efficiency.
Applications:
![]() Sodium & ammonium sulphate
Sodium & ammonium sulphate
![]() Sugar
Sugar
![]() Coal
Coal
![]() Inorganics
Inorganics
![]() Crystals
Crystals
![]() NPK Fertilizer
NPK Fertilizer
Spray Dryers
Principle of Operation:
- Spray drying involves the atomization of a liquid feedstock into a spray of droplets and contacting the droplets with hot air in a drying chamber.
- The sprays are produced by either rotary (wheel) or nozzle atomizers. Evaporation of moisture from the droplets and formation of dry particles proceed under controlled temperature and airflow conditions.
- Powder is discharged continuously from the drying chamber. Operating conditions and dryer design are selected according to the drying characteristics of the product and powder specification.
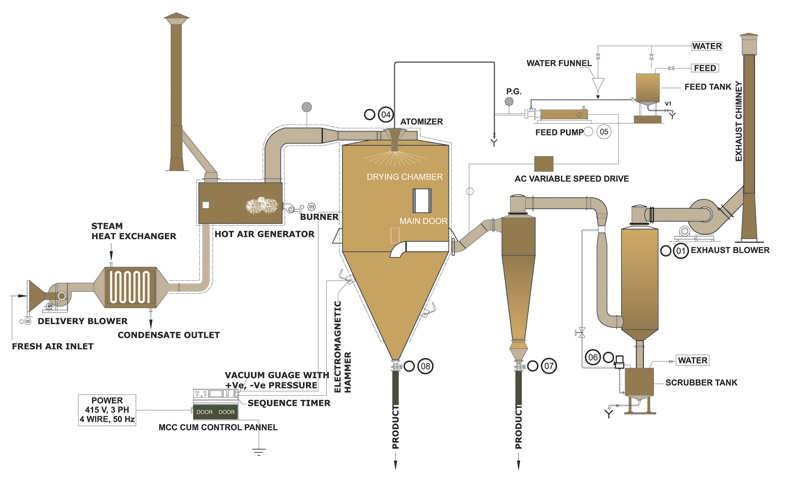
Advantages:
![]() Best product quality
Best product quality
![]() Hygienic design
Hygienic design
![]() Low energy consumption
Low energy consumption
![]() Easy switch over to a different product
Easy switch over to a different product
![]() Long operation time between cleaning
Long operation time between cleaning
Applications:
![]() Food: milk powder, coffee, tea, eggs, cereal, starch and starch derivatives, vitamins, enzymes, stevia, colourings
Food: milk powder, coffee, tea, eggs, cereal, starch and starch derivatives, vitamins, enzymes, stevia, colourings
![]() Pharmaceutical: antibiotics, medical ingredients, additives
Pharmaceutical: antibiotics, medical ingredients, additives
![]() Industrial: paint pigments, ceramic materials, catalyst supports, microalgae
Industrial: paint pigments, ceramic materials, catalyst supports, microalgae
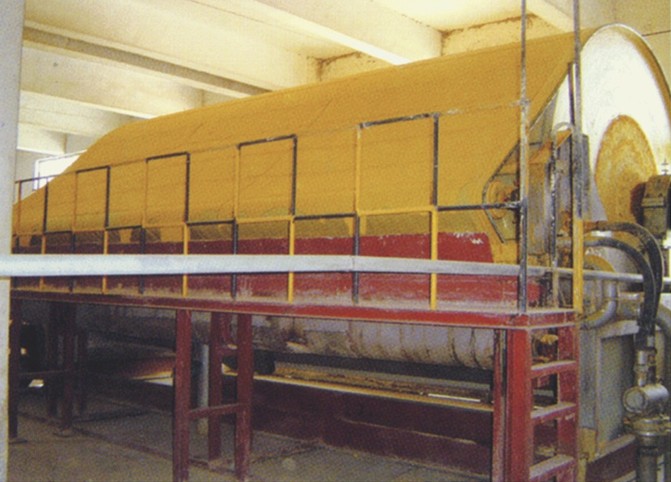
Belt Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- Hot air is passed through the moving porous bed of the wet material.
- The moisture is transferred from the wet particles to the hot air. The material becomes progressively dry as it traverses along the length of the belt dryer.
- The humid air is exhausted via ID fan.
Advantages:
![]() Suitable for granular, fibrous, preformed,
Suitable for granular, fibrous, preformed,
extruded wet materials.
![]() Can handle wet material with both surface
Can handle wet material with both surface
and bound moisture.
![]() Uniform drying
Uniform drying
![]() High energy efficient
High energy efficient
![]() Low power consumption
Low power consumption
![]() Continuous operation
Continuous operation
Applications:
![]() DDGS
DDGS
![]() Agro products
Agro products
![]() Pigments
Pigments
![]() Charcoal
Charcoal
![]() China clay
China clay
![]() Magnesium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate
![]() Zeolites
Zeolites
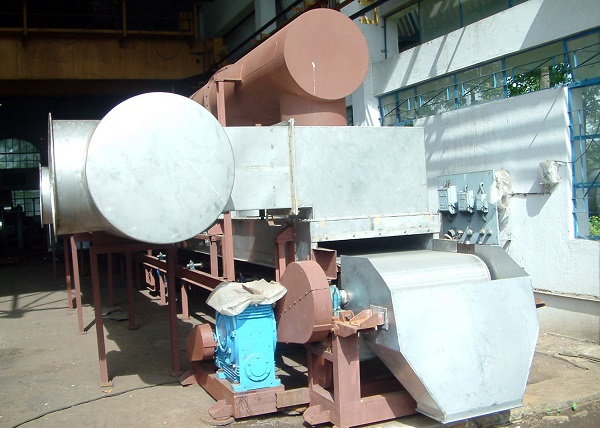

Rotary Vacuum Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- Rotary Vacuum Dryer (RVD) is a cylindrical jacketed vessel with a central agitator having specially designed blades.
- The blades of this Rotary Vacuum Paddle Dryer (RVPD) are so designed that they sweep the entire internal surface and at the same time turn the material so that all the particles are in contact with the heated surface.
- A vacuum Pump of adequate capacity is provided & fitted to the receiver of these rotary vacuum dryers to create the vacuum in the dryer shell through the Receiver, Condenser and dust catcher.
Advantages:
![]() Suitable for drying materials which are heat sensitive, as low temperature for drying can be maintained by high vacuum.
Suitable for drying materials which are heat sensitive, as low temperature for drying can be maintained by high vacuum.
![]() Lowest energy consumption compared to any other batch type dryer due to higher differential temperatures.
Lowest energy consumption compared to any other batch type dryer due to higher differential temperatures.
![]() Higher Thermal Efficiency
Higher Thermal Efficiency
![]() Higher recovery of solvents
Higher recovery of solvents
Applications:
![]() Heat sensitive products
Heat sensitive products
![]() Polymers & solvent
Polymers & solvent
recovery
![]() Insecticides
Insecticides
![]() Pesticides
Pesticides

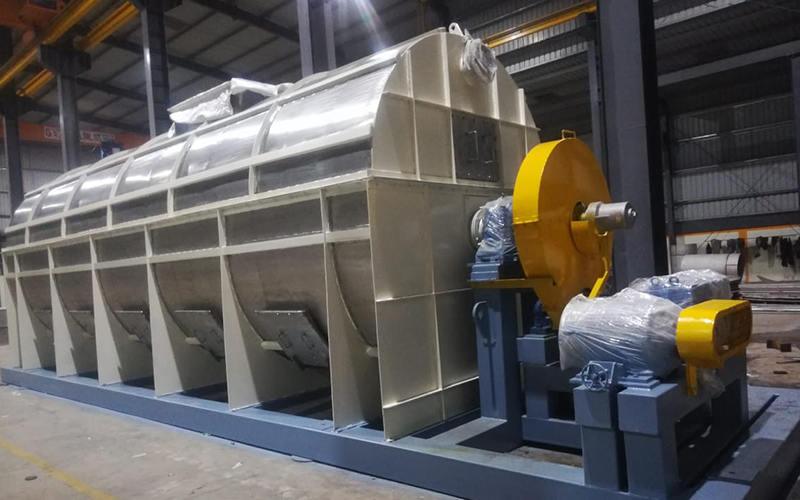
Paddle Dryer
Principle of Operation:
- Paddle Dryer are highly efficient, mechanically agitated, indirect heat transfer devices that add or remove heat from a process mass.
- Dual counter-rotating shafts with unique intermeshing wedge shape paddles produce intimate mixing and optimize heat transfer.
- The use of hollow paddles for heat transfer results in a compact machine. The heat transfer medium: steam, oil, thermal fluid, water, or glycol is isolated from the process mass.
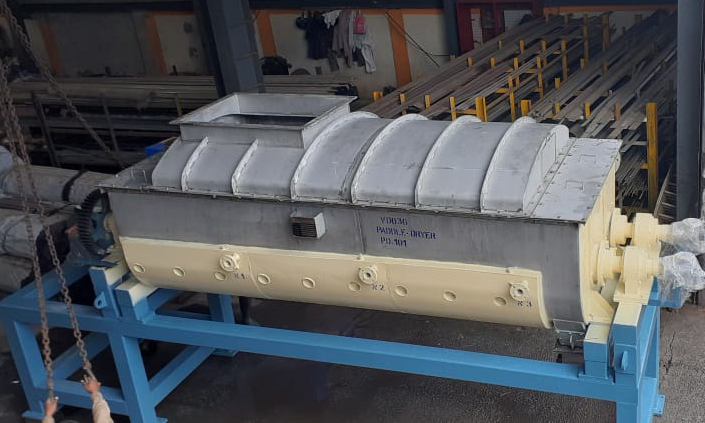

Advantages:
![]() Dryer size is minimized, due to the large heat transfer area per volume.
Dryer size is minimized, due to the large heat transfer area per volume.
![]() Slurry with high viscosities can be treated.
Slurry with high viscosities can be treated.
![]() The wedge shaped paddles goes into the powder to enhance contact to the heat transfer area.
The wedge shaped paddles goes into the powder to enhance contact to the heat transfer area.
![]() Heat transfer coefficient is relatively high due to the good mixing.
Heat transfer coefficient is relatively high due to the good mixing.
![]() Residence time distribution is sharp and the powder is uniformly dried.
Residence time distribution is sharp and the powder is uniformly dried.
![]() Available under the vacuumed condition as well, for materials which are sensitive to high temperatures.
Available under the vacuumed condition as well, for materials which are sensitive to high temperatures.
Applications:
![]() ETP sludge
ETP sludge
![]() Magnesium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate
![]() Magnesium sulphate
Magnesium sulphate
![]() PHBA
PHBA
